
Polymer additive manufacturing (AM) is a cutting-edge 3D printing process that brings digital designs to life by building objects layer by layer using Polymer materials. This technology offers remarkable precision and speed, enabling the transformation of ideas into physical products with ease. It encompasses diverse techniques and materials, allowing for customization based on specific object properties, such as complex geometries, high strength, durability, lightweight strength, or biocompatibility.
Digital Manufacturing and Design for AM are the new tools being used in the forefront of the manufacturing industry. Wipro 3D offers end-to-end services for all your 3D printing requirements. With a combined experience of more than 100 years, our team of dedicated experts help you achieve greater value through efficient manufacturing and streamlined supply chains supported by hassle-free logistics.
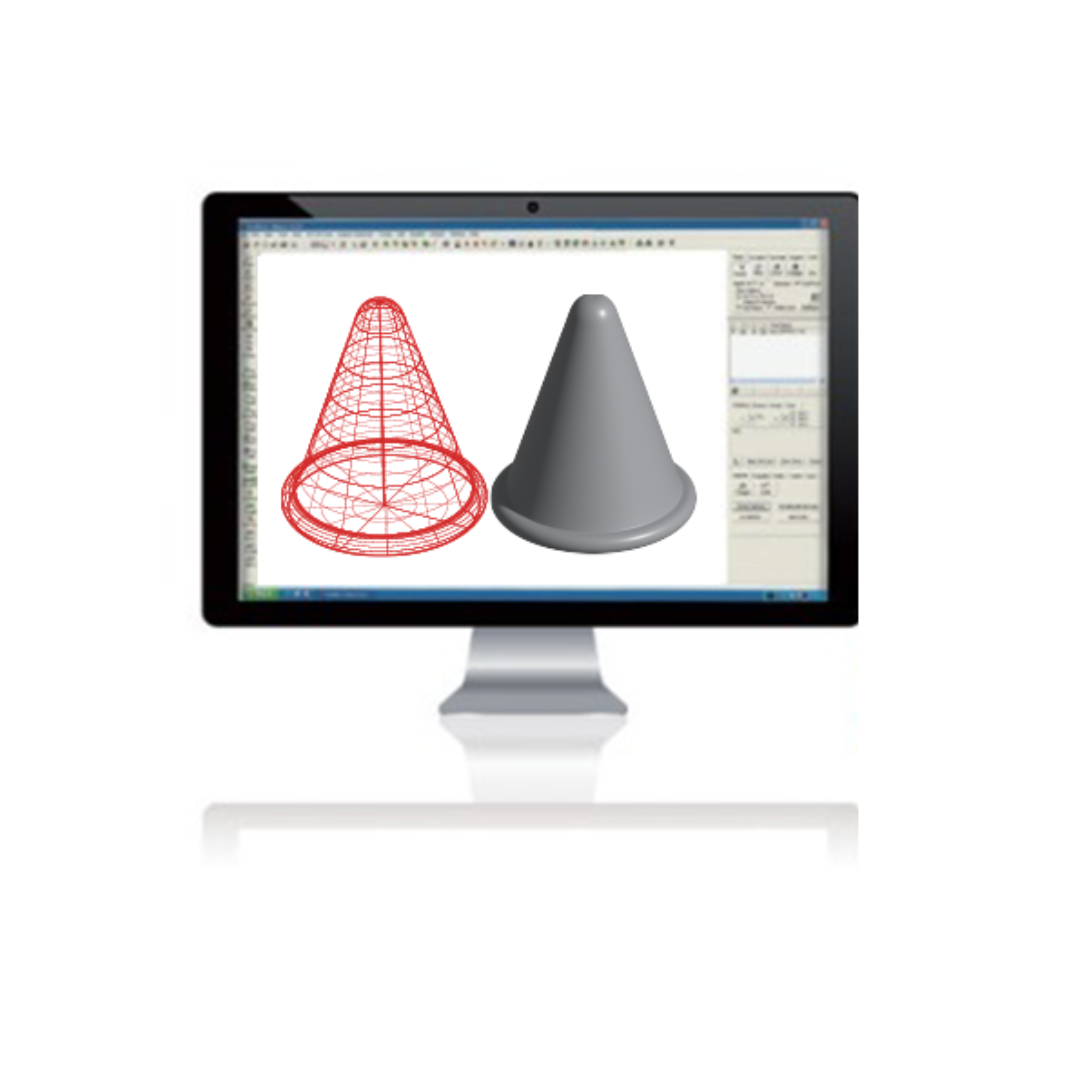
Developing a 3D design of any model using a creative mind with endless possibilities, including textures, will be overviewed on the screen/software to visualize the realistic, achievable product. The design will resolve so many end-moment failures with practical reasoning before 3d printing of any product.
The choice of technology depends on the desired properties of the 3D-printed object, as well as the specific application. For example, FFF is a good choice for creating functional prototypes, while DLP is a good choice for creating high-resolution objects with complex geometries. Polymer 3D printing technologies dominate the additive manufacturing industry as the preferred technology for producing end-use parts, functional prototypes, and complex geometries1. Some common polymer 3D printing techniques include Vat Polymerisation, Material Extrusion, Powder Bed Fusion, Material Jetting, etc.

Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) is an advanced 3D printing process by HP, developed in 2016. It swiftly produces functional nylon prototypes and end-use parts, with quality surface finishes and fine feature resolution. Compared to selective laser sintering, MJF offers more consistent mechanical properties. The technology spreads a layer of powder, deposits fluid in desired locations, and fuses the areas, creating intricate parts with powdered thermoplastics at high speed. Thousands of layers are bonded into a solid functional component using selective fusing and detailing agents.
Materials used for MJF 3D printing can be divided into two categories:
Rigid plastics: These include Nylon PA11, Nylon PA12, and PP. These materials are strong and durable, making them ideal for producing functional prototypes and end-use production parts.
Flexible plastics: This category includes Estane 3D TPU M95A, which is a thermoplastic polyurethane material. This material is flexible and has good impact resistance, making it ideal for producing parts that require flexibility.







Polymer Additive Manufacturing has a wide range of applications across many different industries. It is used to fabricate high-tech industrial products such as aerospace, medical/dental, automotive, and electronic components, as well as consumer products for home, fashion, and entertainment. Advancements in polymeric materials continue to offer new possibilities for the manufacturing industry.

WIPRO 3D F300-2 printer comes with a robust system design meant for reliability and quality. This machine provides excellent print quality and outstanding performance. This best-in-class Industrial Grade 3D printer is designed and manufactured in India.
Polymer additive manufacturing (AM) is a process of creating three-dimensional (3D) objects from digital designs by depositing successive layers of polymer material. The most common polymer AM processes are Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
The best polymer AM process for you will depend on your specific needs and requirements. If you are looking for a quick and inexpensive way to create prototypes, then FFF may be a good option. If you need a more accurate and precise process, then DLP may be a better choice.